Vedas
Rigveda (ऋग्वेद) – The Veda of Hymns
📅 Estimated Period: 1500–1200 BCE (oldest of the Vedas)
📘 Content:
- Contains 1,028 hymns (suktas) in 10 books (mandalas).
- Composed primarily of praises to deities such as Agni (fire), Indra (war/thunder), Varuna (cosmic order), Soma (sacred drink).
- Rich in poetic meter and metaphysical symbolism.
📜 Purpose:
- Liturgical use in sacrificial rituals.
- Invocations to gods for prosperity, rain, protection, and victory.
🧠 Philosophical Aspects:
- Contains early concepts of cosmology, natural forces, and the origin of the universe (e.g., the Nasadiya Sukta).
- Lays the groundwork for later Upanishadic thought.
Yajurveda (यजुर्वेद) – The Veda of Ritual Formulas
📅 Estimated Period: 1200–1000 BCE
📘 Content:
- Consists mainly of prose mantras and ritual formulas.
- Divided into two major versions:
- Shukla (White) Yajurveda – Has a more systematic arrangement.
- Krishna (Black) Yajurveda – Contains both verses and explanations interspersed.
📜 Purpose:
- Provides detailed instructions for Vedic rituals, especially Yajnas (sacrifices).
- Includes procedures for Agnihotra, Ashvamedha (horse sacrifice), Rajasuya (royal consecration), and Somayajna.
🧠 Philosophical Aspects:
- Rituals are linked to the cosmic order (Rta).
Emphasis on Dharma (duty) and correct performance of sacrificial acts.
Samaveda (सामवेद) – The Veda of Melodies
📅 Estimated Period: 1200–1000 BCE
📘 Content:
- Consists of chants and melodies, mostly derived from the Rigveda.
- Has about 1,875 verses, but only about 75 are original, the rest are repetitions.
- Divided into:
- Purvarchika (first part)
- Uttararchika (later part)
📜 Purpose:
- Designed for musical chanting during Soma rituals.
- Recited by Udgātṛ priests using specific melodic patterns.
🎵 Musical Significance:
- Considered the origin of Indian classical music.
- Uses svara (tonal notes) and elaborate intonations.
Atharvaveda (अथर्ववेद) – The Veda of Everyday Life
📅 Estimated Period: 1000–900 BCE
📘 Content:
- Contains 730 hymns with about 6,000 mantras in 20 books.
- More diverse and practical in nature.
- Deals with healing, exorcism, blessings, curses, magic, domestic rituals, and kingship.
📜 Purpose:
- Focuses on mundane and spiritual well-being.
- Used by Brahmaveda priests in rituals not covered in the other Vedas.
🧠 Philosophical Aspects:
- Contains early philosophical and medical thought.
- Includes hymns to Prana (life-breath), Mind (Manas), Time (Kala), etc.
- Basis for Ayurveda (ancient Indian medicine).
Structure of Each Veda
Each Veda is divided into four parts:
- Samhitas – Core hymns and mantras
- Brahmanas – Ritualistic instructions and commentary
- Aranyakas – "Forest texts" for hermits; transition from ritual to meditation
- Upanishads – Philosophical teachings; foundations of Vedanta
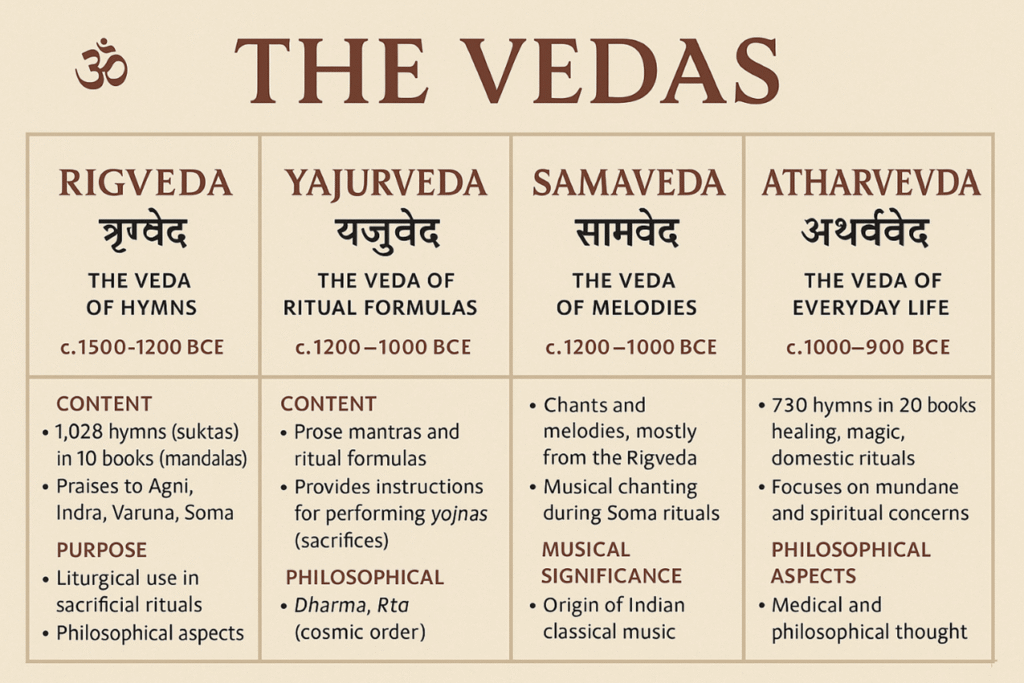
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Rigveda | Yajurveda | Samaveda | Atharvaveda |
| Focus | Hymns & Praise | Rituals & Sacrifice | Melodic Chanting | Everyday Life & Magic |
| Tone | Poetic, Spiritual | Instructional, Ritualistic | Musical, Ceremonial | Practical, Mystical |
| Main Deities | Agni, Indra, Soma | Agni, Indra, Vishnu, etc. | Agni, Soma | Prithvi, Kala, Rudra, etc. |
| Role in Rituals | Recited by Hotri | Recited by Adhvaryu | Sung by Udgātṛ | Used by Brahmaveda priest |
| Modern Influence | Philosophy, Cosmology | Dharma & Ritual Practice | Music, Chanting | Ayurveda, Folk Traditions |